Chromosomes
Our genes are lined up on chromosomes, which come in 23 pairs (46 total). Half of a child’s chromosome comes from one parent, the other half comes from the other parent
22 of the pairs look very similar, if not identical. These are called autosomes. The other 2 chromosomes are called sex chromosomes, and are X and Y. Females have two X chromosomes, while males have one X and one Y. 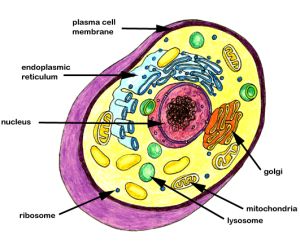
Most living organisms are made up of cells. These cells contain a nucleus that contains a substance called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). DNA is wrapped together to form structures called chromosomes. Most cells in the human body have 23 pairs of chromosomes, making a total of 46. You received half of your chromosomes from your mother’s egg and the other half from your father’s sperm cell. The two chromosomes of a pair (except for the sex chromosomes) contain the same genes, but the genes have small differences. A male child receives an X chromosome from his mother and a Y chromosome from his father; females get an X chromosome from each parent, these are called sex chromosomes. You don’t necessarily end up with a matching pair. Typically females have two X chromosomes and males have an X and a Y. Mothers always pass an X chromosome on to their children. Whether your father passes on his X chromosome (leading to a pair of X chromosomes) or his Y chromosome (making a mixed set) determines your sex. Though most adult cells contain two sets of chromosomes, sperm and egg cells are different. These special cells have just one chromosome from each pair. When a sperm and egg cell join together at fertilization they create a single cell with two complete sets of 23 chromosomes. This single cell divides to create new cells, over and over, forming the body of developing child. If you have children, the same events created them. But because the egg and sperm production processes are random, your children didn’t get the same set of chromosomes from each parent.
always pass an X chromosome on to their children. Whether your father passes on his X chromosome (leading to a pair of X chromosomes) or his Y chromosome (making a mixed set) determines your sex. Though most adult cells contain two sets of chromosomes, sperm and egg cells are different. These special cells have just one chromosome from each pair. When a sperm and egg cell join together at fertilization they create a single cell with two complete sets of 23 chromosomes. This single cell divides to create new cells, over and over, forming the body of developing child. If you have children, the same events created them. But because the egg and sperm production processes are random, your children didn’t get the same set of chromosomes from each parent.
Sections or segments of DNA that are carried on the chromosomes determine specific human characteristics, such as height or hair color. Cells can sometimes contain changes or variants in the information in their chromosomes. This is called a mutation, and it often occurs when cells are aging or have been exposed to certain chemicals or radiation. Fortunately, cells usually recognize these mutations and repair them by themselves. Other times, however, they can cause illnesses or diseases. And if the gene mutation exists in egg or sperm cells, children can inherit the mutated gene from their parents.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T76usaEe7yE
http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/handbook/basics/chromosome